Our team at Lazy River Products is proud to bring you New England’s best cannabis-based options – from concentrates, to premium flower, edibles and topicals, we’re here to be your #1 destination for all of your adult-use cannabis needs. We also fully believe in the power of information and education when it comes to providing people with the proper tools to help remove the stigma that has been associated with marijuana for far too long.
If you’ve been following along with our blog, we’ve recently covered such crucial topics as Delta8 and minor cannabinoids — and while it’s certainly important to understand the cannabis-derived compounds we’re putting in our bodies — it is just as important to pay attention to and learn about the various internal systems and functions that interact with the above-mentioned compounds to provide wellness.
The discovery of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) heralded monumental progress within the world of alternative self-care. Read on as we discuss the ECS, its particulars, and some key players on the journey to its discovery.
What is the Endocannabinoid System (ECS)?
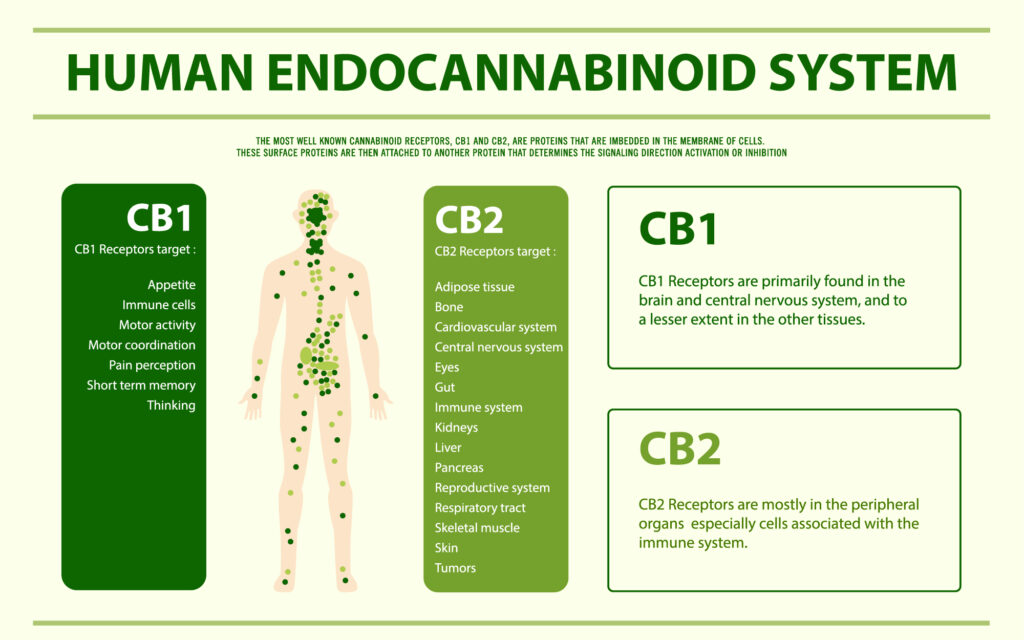
First, let’s talk about the basics of the endocannabinoid system. Present throughout our bodies, the ECS is a complex cell-signaling system that was identified when researchers were exploring the well-known compound, THC. While more research still needs to be conducted, researchers have shown that the system helps to regulate functions such as reproduction and fertility, memory, appetite, mood, and sleep, among others. The endocannabinoid system is made up of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids.
Who is Responsible for Discovering the Endocannabinoid System?
As we get further into this exciting new era of legalized cannabis, it’s also important to understand how far we’ve come, and who is responsible for helping to get us here. The discovery of the endocannabinoid system can be credited to researchers at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
In 1992, Dr. Lumir Hanus and Dr. William Devane discovered the endocannabinoid anandamide and subsequently 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) among other lesser known endocannabinoids. This vital search for the pathways and functions of cannabinoids and endocannabinoids led researchers to uncovering an “unknown molecular signaling system within the body that is involved in regulating a broad range of biological functions.” – or what is now known as: The Endocannabinoid System.
The Endocannabinoid System: A Timeline
For some perspective into the tremendous amount of work that has gone into attempting to study the cannabis plant, below is a helpful timeline of major discoveries within the scope of hemp and cannabis research – leading up to and following the discovery of the endocannabinoid system:
1988 – Cannabinoid Receptor CB1 – this discovery was hailed as a tremendous breakthrough in the world of medical science.
1992 – Endocannabinoid Anandamide – the first endocannabinoid discovered, binds to CB1 and protects neurons.
1993 – Cannabinoid Receptor CB2 – helped to illuminate the process by which the body regulates inflammation.
1995 – Endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) – found more abundantly throughout the body than anandamide, involved in regulating a wide scope of brain/body functions.
1997 – Metabolic Enzymes FAAH & MAGL – discovered nearly 10 years after the CB1 receptor was first identified, metabolic enzymes help to regulate endocannabinoid activity.
1998 – Entourage Effect – important because it underscored the importance of interaction between terpenes, cannabinoids, and other cannabis plant compounds to create a more potent effect on the endocannabinoid system.
1999 – TRP “TRIP” Ion Channels – (transient receptor potential) ion channels, they function as cellular sensors.
2001 – Retrograde Signaling – important because it showed that endocannabinoids have their own form of intracellular communication.
2005 – PPARS Nuclear Receptors – it was shown for the first time that cannabinoid compounds bind to “PPAR-gamma”, which is a receptor that is located on the surface of the cell’s nucleus.
2009 – Fatty Acid Binding Proteins – responsible for transporting anandamide, 2-AG and various lipid compounds through the cell’s internal ecosystem.
2012 – Mitochondria – CB1 receptors discovered on membranes of mitochondria, illuminated the endocannabinoid system and cell function.
2013 – The Endocannabinoidome – introduced as an “enlarged endocannabinoid system” with fatty acid-derived lipids present, in addition to anandamide and 2-AG.
As you can see from the above-mentioned discoveries, the world of cannabis research isn’t showing any signs of slowing any time soon, which is great news for wellness and self-care.
Here at Lazy River Products, we’re excited for the future of our brand, and for the future of legal cannabis and hemp in the great Commonwealth of Massachusetts, and beyond.
For the latest LRP updates, be sure to subscribe to our Newsletter here, or at the bottom of this page.
Always consult a physician before making any changes to your health or fitness regimen.



